FIRST AID
FIRST AID

Choking
Symptoms
Your 2 year old is eating peanuts and running around. Suddenly, he starts coughing violently. There is a strong possibility that he has inhaled the peanut into the windpipe, resulting in obstruction to the free flow of air.
Do not panic. Coughing might help in expelling the peanut. Sometimes, if the obstruction is more severe, due to foreign object or food, he may not be able to talk normally and may turn blue. Treat this as an emergency and act quickly as possible. Sometimes, a little water or milk or soup or any other liquid tend to go into the wind pipe and the child coughs to stop that or to expel the little liquid that might have gone into the wind pipe.This need not be a cause of worry.
Management
Step 1
If your small infant has difficulty in breathing and is becoming blue, shout for help. Lay him in a head down position on your forearm. Let your arm rest on your tilted thigh with his head just below your knee.Then give 4 rapid blows on the back with the heel of your other hand between the 2 shoulder blades. It may be inconvenient to rest an older infant on the arm. Lay him face down on your lap with the head towards the ground and supported with one hand.
Step 2
If you find no improvement put him on the floor on the back. Using 2 or 3 fingers, give 4 rapid chest thrust over the breastbone lying in the center of the chest.
Step 3
If you can now see the foreign object or food in the child's mouth and feel confident that you can easily remove it, pluck it out with your finger.
Step 4
If the child is not breathing follow step 3 with mouth to mouth breathing etc.
Step 5
Keep repeating step 1 and 4 till the child improves or you get some medical help.
The Heimlich Man oeuvre to help an older child with choking.
Stand behind the child and wrap your arms around the waist. Make a fist with one hand and grasp it with other hand . Put your fisted hand on the other upper abdomen just below the breast bone of his chest. Then give abdomen thrust by pressing into the abdomen with a sudden spring upward jerk. You may have to do this repeatedly (up to dozen times) for him to bring a foreign object. If the child is unconscious, give the abdominal thrust with the child lying down.
Cardiac pulmonary resuscitation and mouth to mouth breathing may be required if the child is not breathing.
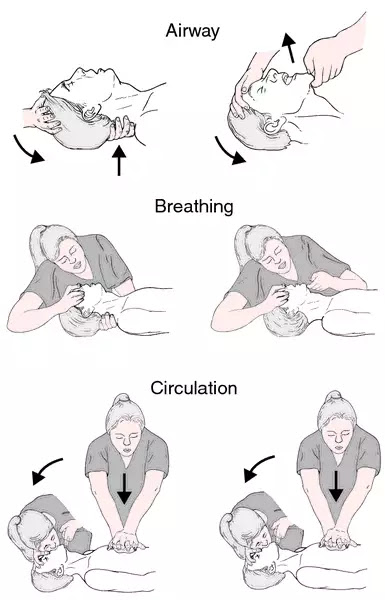
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (C.P.R)
Check for breathing not pulse
Look for any sign of movement and check if the patient is breathing or coughing. If these are absent, call for an ambulance and start for chest compression.
Positioning Hands
Compressing and releasing the chest helps force blood out of the heart and into the rest of the circulatory system. Simply place your hands between the victim's nipple to locate the sternum.For children over 8 years, perform 15 compression before giving 2 rescue breaths.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is an emergency procedure that combines chest compression often with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest.
Mouth to Mouth breathing
Timely help can save life. You must practice the technique in advance.. Have someone call for an ambulance or a doctor, while you start on procedure.
Mouth to mouth breathing in which you exhale into victim's mouth should be learnt. But if you are unable or unwilling to give the mouth to mouth resuscitation, chest compression alone should increase the victim's chance of survival, especially if medical help is imminent.
Cardiac Massage in an infant
Steps to be followed if the child stops Breathing
Step 1
Shout for help to get an extra hand and to summon a doctor.
Step 2
In a case of a child, clear the mouth. Check if anything is struck in the mouth or throat. Pull the tongue forward. Remove any foreign object or food, that can be removed easily with your fingers. If removal seems difficult, choking procedure to be followed.
Step 3
Let the child lie on his back on the ground or any other firm surface like a strong table. Tilt his head back so that the tip of his nose faces the roof or sky Open his mouth wide.
Step 4
If he is still not breathing, start mouth to mouth breathing. For this, take a deep breath. For an infant, place your mouth over his mouth as well as the nose, closing your mouth firmly over them so that no air leaks.Then, blow gently to make sure that his chest rises a little. Do not blow with too much force in an infant, because you may rupture his lungs.
In case of an older child, pinch his nostrils with one hand and place your mouth only on his mouth. Breath into the child's mouth forcefully to ensure some lifting of his chest. Give 2 such breaths.
If the chest is not moving, follow step 2 again.
If the chest rises with mouth to mouth breathing, remove your mouth from his mouth and after every breath, take a deep breath, and breath again into his mouth at a rate of about 20 breaths per minutes until he starts breathing on his own. This effort may be needed for about an hour.
Step 5
Sometimes, the heart also stops beating in such a situation. After the first two breaths, check the pulse. In small infants, put two fingers gently to feel for the pulse in front of the elbow. In older children, feel for the pulsation in the neck a little away from the windpipe at the level of the Adam's apple.
If you cannot feel the pulse, you must begin cardiac (heart) massage by pressing on the breastbone lying in the middle of the chest.
Step 6
If you have help , one of you should do the cardiac massage while the other does mouth to mouth breathing. In case of an infant, press on a breastbone with 3 fingers, placed below the level of the nipple. Press the bone about an inch at a rate of about 100 per minute.
If you are alone, give one breath for every 5 compression (or massage).
For an older child , you may lead to apply more pressure, using the heel of the hand . For an adolescent, you may also need to place the heel of one hand on the top of the other hand and then press down about 1 1/2 inches.
Continue this exercise until you can feel the pulse or until you are sure that the person is dead. It is worth trying this for half an hour to one hour before you give up.
C.P.R and Mouth to Mouth Breathing and Drowning
If a child is not breathing on his own, follow the same procedure as given above,under C.P.R and mouth to mouth breathing. Do not waste precious time trying to get water out of his chest. In fact the person trying to rescue the child is advised to start mouth to mouth breathing as soon as he reaches waters shallow enough to stand in.
Abrasion or Scratches
Scratches: These are slight injuries that happen when a sharp object, like a fingernail or thorn, scrapes along your skin the way a pencil scrapes across paper. Abrasions This is a scrape that happens when the skin is rubbed away.
An abrasion is a minor injury, which needs to be cleaned properly to remove dirt, a possible source of infection. Put the injured part under running tap water or pour water from a glass. Wash your hands and clean the wound with soap and water. No medicine is needed to clean the wound, nor is the use of spirit or iodine.
If the child's booster dose of D.P.T (triple antigen) or dual antigen (D.T) is due, give it now. If he about 10, give him an injection of Tetanus Toxoid. For instance if he has been given D.P.T (which contains Tetanus Toxoid) at the age of 2 and meets with an accident at 3, there is no need to give Tetanus Toxoid.
Dressing is not needed, however if you feel that the wound might not remain clean or that it may attract flies, cover it with a sterile piece of gauze, available from the chemist. Keep it in place with a clean bandage or a clean piece of cloth.. Check the wound daily and change the gauze. If the bandage or a gauze stuck to the wound, pour boiled and cool water to remove it.
If the wound is oozing from the beginning, apply an antibiotic skin ointment on it and than put a gauze over it . If the ointment is not easily available , just sterile gauze will solve the purpose. Once the scab is formed there is no need to cover the wound.
Cuts
Stop the bleeding if there is any. Apply pressure on the site with a clean cloth. Sterile gauze available in packets with the chemist is preferable. Keep pressing at the site for at least five minutes. If the bleeding reoccurs, press again. Most bleeds can be stopped by this simple method. If the bleeding is not severe, wash your hands with soap and water before touching the child. Clean the wound with water. Stitches may be required if the edges of the wound cannot be brought together. If the wound is deep or is more than half an inch long, let your doctor decide.If you think that stitches may be needed, it is better to see your doctor within 8 hours of the injury. if bleeding continues inspite of pressure on the cut, seek medical attention.
Bleeding
Minor cuts and scrapes usually stop bleeding on their own. If they do
not, apply gentle pressure with ice cubes or with clean cloth or
bandage. If bleeding persist, seek emergency assistance.
Apply a thick paste of turmeric powder in water, and cover the
wound.(check there is no glass pieces inside). Exposure to air speeds
healing, but bandage can help keep the wound clean and keep harmful
bacteria out,
Have the injured person lie down. If possible position of person's
head , slightly lower then the trunk or elevate the legs. This
position reduces the risk of fainting, by increasing blood flow to the
brain. If possible elevate the site of bleeding.
Applying a paste of sandal wood powder is helpful in a case of
external bleeding.It stops the bleeding and also heals the
wound.
Drinking a cup of warm milk with half tsf turmeric powder and
a pinch of saffron or alum.Added to it is also very good healing
drink.It also act as pain reliever.
Bleeding can be due to cuts, nosebleed,vomiting in blood, blood in stools or splitting of blood.
Electric Shock
Prevention of accidents due to electric appliances
Management
Step 1 Switch off the power or pull out the plug. If this is not possible, remove the wire from the child with any piece of wood. If that is not handy , rope up a magazine or use a jacket or a rope. Never use your bare hands.
Step 2 If the child is alert and has no burns, just hug him.
Step 3 If burns are visible, visit a doctor to have wounds dressed and also to rule out damage to internal organ.
Step 4 In case of severe burns or damage to the organs, the child may need to be hospitalized.
Step 5 In extreme cases, the child can have, cardio-pulmonary arrest. His heart stops beating and the child stops breathing. In that case, do not waste a moment. Start mouth to mouth breathing discussed under that heading.
Step 6 Some children can get severe convulsions with resultant injuries, including fracture of the spine. Such children should be handled carefully and shifted to the hospital under careful medical supervision.
Foreign Body in the ear
An insect or a grain or other foreign object may be lodged in the child's ear.
Management
In case of an insect, do not try to and remove it until you have put a few drops of warm coconut oil into the ear. If it does not come out easily, flush it out with warm (boiled and cool) water filled in a syringe (without a needle).
With a grain or any other foreign body lodged in the ear , remove it if you can easily do it. Take the child to a doctor if you are unable to do this. If this is not possible, try to flush it out with a syringe filled with warm saline water. Flushing with water should not be undertaken if the child had otitis media in the recent past.
Head Injury
While you are waiting for a doctor, attend to any external injury. If you notice any bump on the head, it is due to external bleeding between the scalp and the skull. Apply gentle pressure with ice in a hand towel or any piece of cloth for 15-20 minutes. If there is a cut on the scalp, attend to it as advised under the section on cuts. If you suspect that the child might have also injured his neck, do not move him, wait for doctor or the ambulance to arrive and let the experts carry the child safely to the hospital. Careless handling of a child with injury to the neck can result in serious damage to the spinal cord.
Hospitalization and test
Let your doctor decide if X-ray if the skull or a brain scan are needed. If the soft spot (anterior fontanel) in a small infant is open, doctor may decide to go for a simple procedure called sonography of the head.
Most cases of head injury need neither hospitalization nor any X-rays. Observation of the child,in most cases for a day or two at home or in the hospital, and examination by your doctor is required. But if one or more of the serious symptoms given above are present, do not delay matters and let the doctor decide the right course of action for your child.
Vomiting in Blood (Haematemesis)
This could be due to severe bouts of vomiting without any bleeding disorders. It can also be due to drug like aspirin,and certain other pain relieving drugs. Especially if these are taken on an empty stomach. Liver diseases and portal hypertension can give rise to dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach which can bleed.
Blood in stools
This can be due to a fissure caused by hard motions with constipation. In such a case , the hard stools are streaked with fresh blood. A rectal polyp is another cause for passage of fresh blood in the stools. The typical history of that of a child who passes drops of fresh blood after having passes a motion. It could also be due to dysentery, intntussusception and Meckel's Diverticulum.
Splitting of Blood (Haemoptysis)
This could be due to certain diseases in the lungs. Blood trickling from the back of the nose and brought out from the mouth can also be mistaken for haemoptysis.
Management
The child should be taken to a doctor or hospital immediately in these situations;
- If the child is bleeding persistently or profusely.
- If the child is bleeding and has unexplained fever, looks severely anemic, has jaundice, complaints of persistent headache or has disturbed consciousness. Such a child could have serious diseases like leukemia, severe liver diseases, meningitis, or bleeding inside the skull.(intracranial bleeding).
- If there is a history of bleeding in him or other members of the family or bleeding following minor injuries or there is spontaneous bleeding from any site without any provocative factors,. Such a child may have a heredity condition called hemophilia. This needs to be fully investigated.
Gum Bleeding
Squeeze the juice of 1/2 lemon into a cup of water and add 1 tsf of honey. This drink should be taken every morning. Massaging the gums gently with coconut oil also helps.Amla powder 1tsf twice a day daily.Vitamin C
Burns
Prevention of burns is of paramount importance.
Minor burns may cause discomfort, but severe burns can endanger life or lead to crippling deformities.
Treatment
Whatever the extent of burns , first put cold water over the burn. Do not use ice. If cold water is not available , keep pouring tap or stored water. over the area for some times. Remove all clothing from the burnt area. Cover the area with a thin piece of cloth. Do not apply any ointment, ghee or honey without the advice of a doctor. Do not puncture the blisters. Generally doctors leave the small blisters alone. The large blisters are often punctured to avoid accidental rupture and consequent infection.
Let the doctor decide if the child needs hospitalization.. Hospitalization may be considered in case of burns of the face. First and second degree involving more than 25% of the body and burns due to chemicals or electric shock.
The first degree burns, the patient only has redness with or without slight swelling of the skin. Second degree burns cause blisters and much swelling. Third degree burns damage even the deeper layers of the skin. The skin may appear white or charred.
The extent of burn is calculated by the 'Rule of Nine'.
Part of the body Percentage Total Percent
Face 9 (18 in infants) 9
Front and Back 18 36
Upper limbs 9 each 18
Lower limbs 18 each (13.5 in infants)
Perineum 1 1
Grand total 100
In case of extensive burns, do not give anything by mouth to the child until the child has been seen by the doctor. Otherwise, plenty of liquids should be given. If the child has received his usual immunizations (including D.P.T or triple antigen) as per schedule there is no need for tetanus toxoid except for severe burns. when you doctor may decide to give it. If a booster dose of D.P.T (Diphtheria, Pertussis and Tetanus) is due, it can be given. This includes Tetanus toxoid.
Apply egg while locally
Aloe Vera gel with a pinch of turmeric locally. along with ghee or coconut oil.
Ghee is beneficial for burns.
Diarrhea
Add 1 tsf of grated ginger and 1 gram of nutmeg powder to
half a cup of water. Blend them together for a few minutes into
a mixture. Drinking twice or thrice a day help to stop a diarrhea.
Eye Burn
2-3 drops of pure Rose water into the affected eye locally.
This can be used 2-3 times a day. It also help in itchy eyes and
reduce the redness in the eyes.
Boils
Apply cooked onion as a poultice on the boil. A paste
of ginger powder 1 tsf and turmeric powder 1
tsf is also good to apply on boil. either boil
will suppressed or a heas will appear so that the pus
can be drained our easily. Black pepper locally
Bad Breath
Chew fennel seeds after meals.
Drink 1/2 cup of Aloevera juice twice a
day.
Cleanse the mouth with licorice powder until
freshness is restored.
Bones Joints And Muscles Injuries
Injuries to Bone
Fracture in children are not uncommon and usually not serious. For instance, when children learn to walk, they fall frequently and can get the so called 'toddler fracture'. The child avoid putting weight on that leg and tends to limp.These fractures usually heal without any treatment. But if the symptoms persist for more than a day or two, the doctor must be consulted.
Management
If you suspect a fracture (pain local swelling, and lack of movement of the affected limb), make a splint from a piece of wood or folded news paper. Put it under the injured site to prevent movement. Use cold compresses on the site till the doctor sees the child..
If there is a possibility of a fracture affecting the spine or neck, do not move the child yourself. Let the doctor handle the case. If there is bleeding , apply firm pressure on the wound.
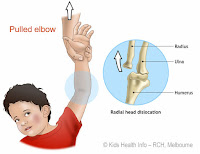
Pulled Elbow
You and your child are holding hands and walking together when he suddenly decides to move away from you. You pull him forcefully towards you. He complains of pain near his elbow, which is slightly bent. Straightening the elbow causes more pain. This is the description of a pulled elbow.These children have rather loose elbow joints. When you pull them , the upper end of bone nearer the arm was pulled towards you, creating a space between this bone and other bones. The tissue nearby slid into this newly created space. When the pull is released, the bone goes back to its earlier position, the tissue gets trapped inside the joint and the child feels pain.
Treatment
It is best to take your child to the casualty ward in a hospital where the doctor will immediately set it right. Once treated the pain will immediately subside. If not the child will probably has some other problem which might need an orthopedic doctors opinion.
Sprains affecting the joints
The common example is a twisted ankle joint. The ligament holding the joints together is either stretched excessively or gets torn. The child feels pain. refuses to walk and a swelling is noticed around the particular joint.
Treatment
As there could be the underline fracture, a medical opinion is desirable. Keep the joint motionless while waiting for the doctor. If you have an elastic bandage, wrap it around the joint, but not too tight. Remove it for a while every 2 hours to make sure that blood flow is not obstructed.
Injuries to the tip of the fingers or nail
This can be very painful and may even lead to a permanent deformity of the growing nail. The tip of the fingernail can get caught in the closing door of the car or at home. Sometimes, the injury is not severe and the child does not complain of much pain. They may not be much swelling either. Such cases can get better without any treatment. The problem arises if you notice swelling or blood is noticed under nail.
Treatment
Such a situation needs urgent medical attention. While waiting for a doctor, give cold compresses with crushed ice in a small hand towel or a piece of cloth. If ice is not available, take cold water and let the finger dipped in it. If the skin is cut, wash it with soap and water and put sterile gauze (available in packets with chemist) on it. If the finger is bleeding a cold compress will help. Too much pressure to stop the bleeding should be avoided as there may also be underlying fractures. Keep the finger a little raised.
The doctor will decide if there is need to remove blood from under the nail by making a small whole in it. If he suspects a fracture , he will ask for X-ray. Consulting an orthopedic surgeon is essential if a fracture is confirmed, or if there is damage to the nail bed, where nail growth takes place.
Injuries to the Muscles
Symptoms
Muscles are strained after a certain activity and exertion. The child may complain of severe pain in one or more muscles. He may not be able to move the affected part, possibly because of bleeding within the muscle that makes it stiff.
Treatment
Raise the limb and gently massage it after after applying hot compresses. In future, let the child start an exercise to which he is unaccustomed gradually and do warm up before any active sports.
Bow legs and knocked knees
Most infants are bowlegged. Similarly most preschool children have knock knees. Both there conditions usually do not need any treatment. The legs become straight in almost all cases before the child starts school.
Knock knee position is demonstrated (left), and the bowleg position is also pictured (right).
Rickets can cause bowing of legs, but in such a case the doctor will also notice other findings suggestive of rickets. The doctor should also be consulted if only one leg is affected or if the bowleg seems to get worse after 2 years of age.
In case of knock knees, if the gap between the ankles, with the child lying down,(legs touching the bed), is more than 10 cm, or if the knock knees persist after 7 years of age, further investigations and treatment may be required.
Snake Bite
Most snakes in our country are non-poisonous, helpful in killing mice and other harmful pests, and should not therefore be killed. It is however important to seek medical advice for all suspected cases of snake bite. It is helpful to know that even when bitten by a poisonous snake , a person may not suffer any ill effects if a venom has been injected into the system.
Treatment
Treatment for snakebite must be prompt. If the snake alive or dead - is available, take it to the hospital, for the doctors to decide, if it is poisonous. Do not panic. Keep the child on an empty stomach.
Do not suck the bite site or make cuts into it. Keep the bite site lower than the level of the heart.; apply a tourniquet or a rubber tube , or any constricting band between the bite side and the heart. To maintain the blood supply, the tourniquet should be slackened for a few seconds at regular intervals of about 10 minutes.
The bitten part should be kept steady. Usually the bite is on the lower limb.As the venom spreads faster on the movement , the child should not be allowed to walk. Carry the child flat on the bite site at a lower level than the heart.
The venom from the sides usually spreads through the lymph vessels lying under the skin. The best way to reduce the risk is to put a pressure bandage on the limbs and to immobilize it with a splint. (Take any clean cloth or a crepe bandage, if available, and apply it over the bite site above it. Then apply a splint- a thin long piece of wood or any other material- that should include joints on either side of the bite. This prevents the use of muscles around the bite site and hence reduces the lymph flow and the speed of the venom.
Paracetamol can be given for pain. Local application of ice reduces the application if pain. Since direct prolonged contact of ice with the skin can result in damage to the underlying tissues, crush the ice and pack it around the bandage.
For poisonous bites, an injection of prevalent antivenom (which protects against venom of all common poisonous snakes) must be given as soon as possible. Do not delay in taking the child to the nearest hospital.
Scorpion Sting
The most dangerous species is the red scorpion, whose sting can cause systemic manifestation, like vomiting, profuse sweating, abdominal pain and agitation.
Treatment
Local treatment with an ice pack in an hand towel or a piece of cloth helps. Apply pressure on the wound with a thick bandage or a piece of cloth to reduce the risk of the spread of venom. Scorpion anti-toxin , if available , should be injected preferably within 2 hours of the scorpion bite. A child with a systemic feature must be hospitalized..
Prevention
Teach your children to turn their shoes upside down before wearing them, specially in a scorpion infestation rural area.
Bites And Stings
Mosquito, Bed Bugs, Bee and Wasp Stings.
A mosquito bite can be recognized by the slightly raised red area with a bite mark at the center. The possibility of bed bugs should be considered if a child start itching soon after a bus or train ride. He has probably been strung by a bee or a wasp if he was in a garden and complains of severe pain and swelling at the site . Sometimes, insect sting may result anaphylactic shock.. Spider bites can also cause problems. similar to bee and wasp sting.
Treatment
Most insect bites subsides within a day or two without any treatment. Calamine lotion helps to reduce the itching. For wasps and bee stings ice packs with a small hand towel or a piece of cloth should be applied locally despite the child's initial protest. Applying vinegar on wasp string and lime on a bee string.
Bee also have a venom sac attached to the stinger, if the stinger is present, it should be scraped with a knife. We should not try to remove it with our fingers otherwise we may squeeze the venom sac and push more venom in child,s system. The stinger of the honey bee is difficult to remove , so it should be left alone.
If the child goes into anaphylactic shock, immediate help must be sought for the emergency.
Prevention
If mosquitoes are a problem at night, keep the windows closed in the evening (when mosquitoes are more likely to enter into the room). Open the windows at night and use a mosquito net that covers the whole bed. Do not use an umbrella type net for small babies; it may close automatically and injure baby.
Avoid using mosquito coils, they can cause chronic cough in some children. 5 -10 ml of Citronella oil be mixed with 100 ml of coconut oil, a cotton swab dipped in oil and kept near the head end of the bed to repel the mosquitoes. The oil can also be used for the skin in place of mosquito repellent creams.
Breathlessness
Take a note when any child breaths over 50 times a minute.
Smaller children normally have a faster rate of breathing than older children, but we should immediately show the child to a doctor if the rate of breathing is as follows:
Up to 2 months of age 60 or more per minutes
2 month to 1 year 50 or more per minute
1 to 5 years 40 or more per minute
Older children 30 or more per minute
To count the respiratory rate, place a watch (with a second's hand) over the chest of a child and count the number of breaths per minutes.
Along with faster breathing, if the spaces between the lower ribs of a child's chest go in as the child breaths, rush to the doctor. If such a child is unable to drink anything, it is an medical emergency and the child should be taken to a hospital immediately.
Common causes:
A few common causes of breathlessness are Pneumonia, asthma, bronchiolitis, stridor associated with a foreign body or serious infection of the throat. Heart failour due to congenital or acquired heart disease.
Bronchiolitis
Symptoms
An infant between 2-6 months of age , having mild cold like symptoms with low fever, may become rapidly ill and restless, develop a severe cough, breath heavily (50 are more breath per minute) start wheezing, and may even become blue. In such a case there is a strong possibility of the child having bronchiolitis. This disease is seen mostly during the winter months. It is due to a viral infection and hence antibiotics are not helpful.
Treatment
Children with bronchiolitis often need hospitalization. An X-ray will be taken.. Oxygen and intravenous fluids may have to be given. . If the chest X-ray shows evidence of a bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics will be prescribed.. If the infants gets more than one attack of the so called 'bronchiolitis' it is possible that he has asthma and not bronchiolitis.
Try and prevent bronchiolitis by keeping children away from those having a viral cold.
Headache
Sinus headache can be
relieved by undergoing sudation after
applying gingelly oil mixed with camphor.
Temporal headache can be relieved by the
application of sandalwood paste to the
temples.
Splinters
A splinter under the skin can be quite painful To remove it, clean the part and soak it in hot water for about 15 minutes. If the splinter is visible, remove it with a pair of tweezers, If not use a needle, which should be either heated on a flame and cooled or wiped with spirit, to take it out.Consult your doctor if you fail to take it out your self.
A secretion of Calotropis gigentis applied for few minutes. remove it with hand.
Emergencies in Children
- Abdominal pain
- Allergies
- Artificial Respiration
- Asthma
- Bites & Stings
- Bleeding
- Bones, joints & muscles injuries
- Breathlessness
- Bulging Fontanel
- Burns
- Choking
- Common cold in an infant
- Convulsions
- Croup
- Crying
- Cuts
- Dog bite
- Diarrhea with dysentery
- Drawning
- Electric shock
- Eye problems, including injury to the eye
- Fractures
- Head injuries
- Hernia
- High Fever
- Mouth to mouth resuscitation
- Nose related problems
- Poisoning
- Rabies
- Scorpion bite
- Snake bite Splinters
- Stridor
- Unconscious child
https://madhuchhandacdmo.blogspot.com/2020/06/first-aid_28.html















.jpeg)
Comments
Post a Comment