Vipaka or Post digestive Taste
Vipaka or Post digestive Taste
(final end product )
Introduction
Effect of Vipaka (Post digestion taste changes) on Doshas.
When the food in the stomach and intestine undergo digestion they undergo taste conversion. This transformed taste is called Vipaka or Nishta Paka. This knowledge helps to understand how food or medicine act in our body. Thus when a substance of particular taste comes in contact with digestive fire they also undergo taste conversion. Final taste obtained in substance after it gets digested For example final end product with different taste is called Vipaka.
Types of Vipaka
Based on conversion of taste of a substance, Vipaka is also of three types :
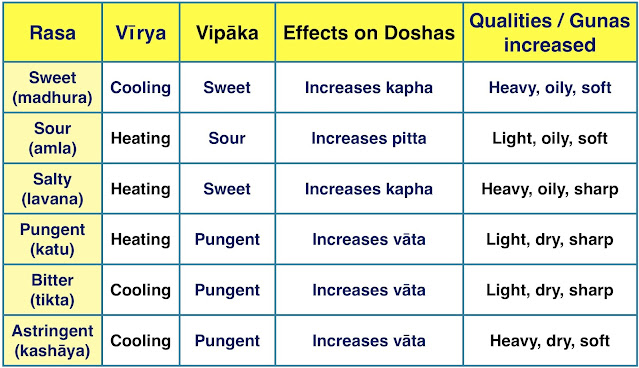
1 . Madhur Vipaka : Madhur Vipaka i.e.Conversion into - Substance having salt and sweet taste get transformed into sweet taste after getting digested by fire. This increases Kapha and mitigates Pitta and Vata.
2 . Amla Vipaka : Amla Vipaka i.e. for example conversion into sour taste.- Only those substance with sour taste get transformed into sour taste after getting digested by fire. Therefore sour taste do not change after digestion. This increases Pitta and mitigates Vata.
3 . Katu Vipaka : Katu Vipaka i.e. for example conversion into Pungent taste. Substance having pungent, bitter and stringent taste get transformed into pungent taste after getting digested. This increases Vata and mitigates Kapha.
Vipāka (PDE or post digestive effect): The end result of digestion. It affects excreta and the dhātus (tissues).
Silent Features
Silent feature of 'Post digestion conversion of taste of substance' and its impact on Doshas.
n Vipaka resembles Avastha Paka but both are different. Avastha Paka explains different phases of digestion of food at various levels of alimentary canal immaterial of taste of food. Vipaka is taste conversion of substances coming in contact with digestive fire.
Avastha Paka or Prapaka or First Digestion.
Avastha Paka is also called the Prapaka which means first digestion. This process takes place during early digestion.
Avastha Paka is applicable for food. Substance having six taste
While Avastha Paka takes place during the process of digestion at different parts of digestive system from mouth to colon.
In Avastha Paka individual taste are not concerned . Food consist of all six taste nd combinations of foods of any taste will undergo a sweet, sour and pungent phases in that order leading to formation of Kapha, Pitta and vata in stomach, intestine and colon respectively, during process of digestion.
Avastha Paka starts in mouth and completes in colon i.e.entire process takes place in alimentary canal . In other terms it starts with mastication of food and ends with formation of feces.
Avastha Paka is influenced by gut fire. In fact sweet phase starts when before food comes in contact with digestive fire.
Vipaka means after digestion
This takes place in later part of digestive process. Vipaka is application for digestion and conversion of medicinal herbs.
Vipaka occurs after completion of digestion. Post digestion taste changes in given substances takes place at the time of absorption of chyle (digestive by-product in intestine.
Action of changed taste of substance will be different from the original taste. Action of former will be permanant one. This holds good with herbal medicines because their impact is more or less or directly on disease process.
Thus change of taste of a substance or herbs post digestion is directly targeted to a disease pathology, pathological site , tissue, or viscera. Example sweet and salt taste will have different impact on body individually but when both are taken together they are converted into sweet taste post digestion. Impact of this changed taste i,e,sweet taste obtained from digestion wil be final impact and different from original taste.
Changed taste of a substance post digestion will have similar impact and action on Doshas like that of Avastha Paka .i.e. Pungent taste obtained after digestion of pungent, bitter nd stringent taste will stimulate and increase vata and mitigate kapha just will be final impact just like pungent phase of digestion.
In Vipaka individual taste will undergo change in taste after coming in contact with digestive fire after digestion has completed.
Vipaka begins after digestion and conversion of particular taste absorbed in intestine and end in making final impact in tissues.
Final phase too does not need digestive fire. Though colon fire has been mentioned it is not a fire by real terms. Re-absorption of water, salts and minerals and consequent drying of end products of digestion leading to formation of feces is depicted in terms of Shoshymana vahni or colon fire.
Vipaka is invariably influenced by digestive fire. Later it is influenced by elemental fires and during final impact wherein they act on body component , is influenced on tissue fires also.
Kapha formed by a Rasa tissue during formation of blood tissue from lymph and formation of Pitta from blood tissue during formation of muscle tissues from blood can be considered due to impact of post digestion change in taste. This Kapha and Pitta are waste and unwanted form of kapha and Pitta while Kapha and Pitta formed during phase wise digestion in gut are supportive in nature form functional component of body.
Sweet sour and salty will increase PittaAstringent, bitter and pungent will increase VataSweet, sour and salty will increase Kapha.
Fruits & Vegetables
Pitta increasing food
Pitta decreasing food
Apple Taste sweet and astringent. Vipaka Sweet
Banana Taste



.jpeg)
Comments
Post a Comment