Abscesses (Pus)
Abscesses/Pus/ विद्रधि / फोड़ा
How does an abscess form?
.jpg) |
| (S. aureus) is a Gram-positive spherical bacterium which on microscopic examination appears in pairs, short chains, or as bunched |
Bacterial infections usually cause abscesses. A bacteria called Staphylococcus causes most abscesses. When bacteria enter your body, your immune system sends white blood cells to go fight the infection. This process causes Inflammation, and the tissue nearby dies. When this happens, a pocket forms and fills with pus, creating an abscess.
Rarely, viruses, parasites and fungi can cause abscesses.
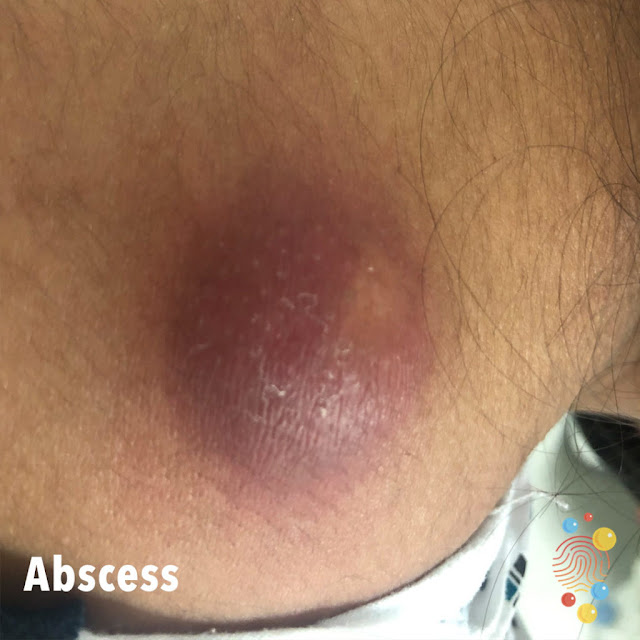
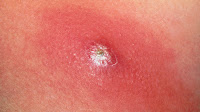
An abscess is a suppurative inflammation where the pus is formed in the tissue cavity. The place is swollen, redden, warm and painful. It may also cause fever in certain cases. Abscess may occur anywhere on the body – on the back, chest, abdomen, groin, etc.
There are also internal abscesses that affect the organs – liver and lung, dental etc., and the suppurative inflammation can also develop between organs. In general abscesses are associated with metabolic disturbances and decreased immunity.
What are the different types of abscesses?
There are many different kinds of abscesses. Abscesses can develop on your skin , in your mouth or around an internal organ.
Skin abscesses
Skin abscesses (cutaneous abscesses) develop under your skin. They’re common and typically easy to treat. Types of skin abscesses include:
- Armpit abscess:
.jpeg)
An armpit abscess can occur when pus collects in your armpit. One common cause of armpit abscesses is a condition called hidradenitis suppurativa. Hidradenitis suppurativa causes red, tender bumps in the skin of your armpits that can turn into abscesses over time. Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a painful, long-term skin condition that causes abscesses and scarring on the skin. The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is unknown, but it occurs near hair follicles where there are sweat glands, usually around the groin, bottom, breasts and armpits.
- Breast abscess:
-

- Cold abscess
As the name suggest abscess is ‘cold’ and non–reacting to the nature. It does not produce hot and painful abscess as seen in pyogenic abscess. Brawny induration, oedema and tenderness are conspicuous by their absence. Only when they are associated with secondary infection a few of these features are present. Cold abscess is almost the sequel of tubercular infections anywhere in the body commonly in the lymph nodes. As the name recommend abscess is 'cold' and nonresponding to the nature. It doesn't create hot and agonizing inflammation as seen in pyogenic abscess.
Cold abscess of Sternum
- Anorectal abscess:
- An anorectal abscess is an abscess located under the skin around your anus or rectum. A perianal abscess is a type of anorectal abscess that affects the skin around your anus. A pilonidal abscess is an abscess in the skin of the crease of your buttocks.
Abscesses in your mouth
Abscesses in your mouth can affect your teeth, gums and throat. A tooth abscess (dental abscess) is an abscess that forms around a tooth. There are various types of tooth abscesses:
- Gingival abscess: Another name for a gingival abscess is a gum abscess. This type of abscess develops in your gums. It doesn’t usually affect your teeth.
- Periapical abscess: A periapical abscess is an infection that forms at the tip of the root of your tooth. This type of abscess can occur due to dental injuries or cavities.
- Periodontal abscess: A periodontal abscess affects the bones and tissues that support your teeth. It usually occurs due to periodontitis or gum diseases.
- Tooth Abscess

Other abscesses in your mouth may include:
- Tonsil abscess: A tonsillar abscess is a pocket of pus behind one of your tonsils. Tonsillar abscesses are most common in adolescents and young adults.
- Peritonsillar abscess: Another name for a peritonsillar abscess is a quinsy. A quinsy is a buildup of pus between your tonsils and the wall of your throat.
- Retropharyngeal abscess: A retropharyngeal abscess is an abscess in the back of your throat. This type of abscess forms when lymph nodes in the back of your throat become infected.
Internal abscesses
Internal abscesses occur much less frequently than external ones, but can develop on your spinal cord, brain and other organs. Internal abscesses are usually harder to diagnose and treat.
- Abdominal abscess: An abdominal abscess is a buildup of pus inside your belly (abdomen). It may be located inside or near your liver, kidneys, pancreas or other organs.
- Spinal cord abscess: A spinal cord abscess is a buildup of pus in and around your spinal cord. An infection on your spine usually causes a spinal cord abscess.
- Brain abscess: A brain abscess is a rare buildup of pus in your brain. An abscess may form in your brain when bacteria from an infection elsewhere in your head or bloodstream or from a wound enter your brain.
- By Physical Examination
- Pus culture and sensitivity.
- Check for Blood sugar Fasting and Post Prandial.
- Check for Tuberculosis for cold abscess.
- Amoebic Liver Abscess : Diagnosis is based on :Stool -ova cyst . Blood culture sensitivity, USG Whole abdomen. Ultrasound which is the gold standard for liver abscess.
These tests may include:
- Ultrasound :An ultrasound is a safe medical imaging test that uses sound waves to create a real-time video of your internal organs.
- CT (computed tomography) scan :A CT scan uses X-rays and computers to create images of a cross-section of your body.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan : An MRI uses a large magnet, radio waves and a computer to create clear images of your organs and body structures.
- Increase in local temperature.
- Redness of the skin over the inflamed area.
- Pain & Tenderness.
- Swelling.
- Loss of function.
- Fever, chills and rigors.
- Excessive sweating.
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Toothache for tooth abscess
- Teeth sensitivity
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Difficulty opening your mouth
For deeper skin abscesses or those inside your body, symptoms aren’t as obvious. Some symptoms relate to the part of your body that’s affected. You may experience:
- Fatigue
- Pain and tenderness.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Excessive sweating
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Diabetes
- External cause is injury.
- Amoebic liver abscess :Diagnosis is based on :Stool -ova cyst . Blood culture sensitivity, USG Whole abdomen.Ultrasound which is the gold standard for liver abscess.Complications can be reduced by early diagnosis. The immuno comprimized host is more likely to develop an amoebic liver abscess. It has abdominal pain and fever. Mortality 20-60%.Treatment : Ant amoebic, Percutaneous Drainage and surgery.
- According to Ayurveda :
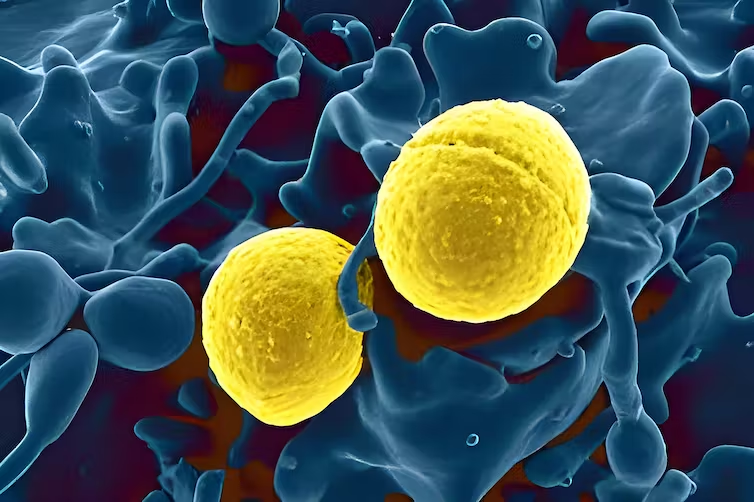 |
| Scanning electron micrograph of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (gold) outside a white blood cell (blue) BSIP/Universal Images Group via Getty Images |
Your skin usually deflects any bacteria it encounters, protecting you from all sorts of infections. However, when you get a bug bite or a rash, some of that bacteria can sneak in, potentially causing serious consequences.
For example, you might develop cellulitis – it’s the most common infection that occurs when bacteria breach the skin barrier. this painful red rash each year. It may happen after a bite or cut or if your skin gets so dry that it cracks and bleeds.
When the infection happens, the area becomes painful, swollen, firm and warm. These symptoms can develop quickly, sometimes in less than 24 hours. It usually affects the feet or legs, but it can affect any part of the body – even your face. You might see red streaks or blisters in the afflicted area, and the skin can become dimply and, above all, very tender.
Most people who get cellulitis are middle-aged or older adults, but kids and younger adults can get it too. Aside from age and bad luck, risk factors include being overweight or having an immune system weakened from diabetes, cancer or HIV/AIDS. Circulation problems, such as long-standing leg swelling, also make people susceptible.
A variety of different bacteria can cause cellulitis. One of the most common culprits is Staphylococcus aureus – often called “staph.” Another common one is the same bacteria that is responsible for strep throat: Group A Streptococcus pyogenes.
Cellulitis is an infection of the deeper layers of the skin, and you can’t catch it from someone else.
If you get it, your physician will prescribe antibiotics and the condition should improve within one or two days. However, the redness may take up to four weeks to fully go away. Do not be alarmed if your skin turns slightly scaly, flaky or wrinkly as the inflammation heals.
Seek emergency care if the affected area doesn’t seem to be clearing up within three days, you run a fever of over 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit, you develop other flu-like symptoms, the redness and pain rapidly worsen or an abscess forms.
To prevent cellulitis, protect your skin by wearing appropriate clothing. You should also wash skin immediately after an injury with soap and water. If you tend to have dry skin, use moisturizers to prevent any cracking.
Why cellulitis matters
Cellulitis can become very serious.
Left untreated, it can spread to your lymph nodes or blood, causing a life-threatening condition called sepsis. Sepsis can affect and even shut down the internal organs, which can be fatal. The bacteria can also spread to the bones or the heart once they enter the blood, with possibly long term consequences.
Doctors and other medical practitioners can diagnose cellulitis by examining your skin. In some cases, doctors may culture or sample the bacteria from the skin or blood to find the culprit. Occasionally, there can be concern that it will form deeper pockets of infection. In those cases a doctor may order a CT scan or ultrasound.
Is it cellulitis or something else?
Just as there’s a danger of not catching cellulitis before it causes more serious problems, there is also a risk that other diseases will be mistaken for cellulitis. This confusion is something we frequently see as dermatologists.
Stasis dermatitis, which is caused by swelling of the legs from leaky vein valves, is the most common condition that looks like cellulitis. Fortunately, the two can typically be distinguished, as stasis dermatitis tends to affect both legs. Cellulitis almost always only affects one leg or arm at a time.
A hematoma, a collection of clotted blood under the skin or other areas, can also occasionally mimic cellulitis. So can gout, a form of arthritis. Like cellulitis, it can be red and painful. However, gout most commonly occurs over a joint.
2 . Kacchapika
Extends over a large area and looks like the back of a tortoise with greater pain.
3 . Jalini
It is hard, displays prominent blood channels on the surface, and has a wide base with an oily discharge emerging through small openings.
4 . Sarsapi
It is not large but is very painful and has mustard seed like boils which suppurates quickly.
5 . Alaji
It is associated with burning sensation which increases with the time of onset and shows other symptoms such as thirst, fainting and fever. It also has a tendency to spread.
6 . Vinata
It causes deep seated pain and appears on the back or abdomen. It is large bluish and saucer shaped with a thick discharge.
7 . Vidradhi / Abscess
A confined pocket of pus that collects in tissues, organs or spaces inside the body is called Vidradhi. The abscess could be cause of imbalance in any of Tridoshas .
"In general abscesses are associated with metabolic disturbances and decreased immunity."
It is important and merits detailed discussion. Vidradhi may be external or internal. The external form is taut and painful and appears on the skin, tendon or muscle. The multiple factors leading to the formation of Vidradhi include unwholesome diet and eating during indigestion, drinking too much wine or wine of poor quality, suppression of natural urges, too much physical activity as well as too much weight, and sheer fatigue. As a consequence dosas are perturbed and assail muscle and blood leading to the formation of deep seated and painful swelling of the glandular type in the cardiac region, lungs, liver. spleen, flanks, kidney, naval, groin and urinary bladder. The inflammation progresses rapidly because blood is contaminated with disturbed doshas.
- Vata Vidradhi– Black In Color Severe Painful , Swelling Different Type, Pus Liquefied.
- Pitta Vidradhi– Reddish In Color, Burning Sensation, Pus Yellowish-Red,
- Kapha Vidradhi– White Yellow In Color, Cold In Touch, Less Painful, Matted Nodes, Pus White
The specific symptoms vary among Vidradhi caused by vata, pitta and kapha, but all share the common symptom of severe pain. The pus from the Vatika Vidradhi is thin rough radish black and frothy while the Pittaja version yields
Abscess which occur in cardiac region, naval and urinary bladder generally result from the disturbance of all three dosas and are fatal. Those in other locations are amenable to treatment by expert physicians. One should loose no time in treating an internal abscess of recent onset, by administrating lubricants and purgatives, this should be followed by management as that for an abdominal lump.
Abscess can occur in obese individuals in absence of diabetes and may not attract attention until they are advanced. Saravika, kacchapika andjalini variety are very painful and occur in obese and kapha laden individuals; sarsapi, alaji, vinata and vidradhi which affects individuals with excess of pitta respond well to curative therapy. On the other hand, the diabetic who has abscesses in the vital organs, shoulder, anus, hands, breast, joints and feet seldom survives.
Abscess may be hard or soft, red, yellow, black, may be large or small, slowly or rapidly progressive and mildly or severely painful. If untreated, they may develop complications such as gangrene, shortness of breath, hiccup, loss of consciousness, and even spread to other parts of the body and cause the failure of vital organs. Therefore physician id obliged to examine each patient carefully in the light of signs and symptoms and make a diagnosis on the basis of the perturbation of vata and other dosas. This should be followed by prompt and appropriate treatment.
Minor skin abscesses may clear up on their own. But you should see your healthcare provider for any abscess that doesn’t go away within a couple of weeks. With treatment, the abscess will have the opportunity to drain properly and clear up. If you don’t get a skin abscess drained, it can continue to grow and fill with pus until it bursts. A burst abscess can be very painful and cause the infection to spread.
Treatment for tooth and other mouth abscesses is especially important. Untreated tooth abscesses can kill you. Untreated infections can spread to surrounding tissues in your body. This can cause serious complications including sepsis and necrotizing fasciitis, which can lead to death.
The outlook for internal abscesses depends on the location and treatment.
If you’ve had surgical drainage for a skin abscess, you should assess your wound each day. You may need to repack the wound with your healthcare provider’s instructions. You’ll have to change your dressing as needed. Any access drainage should stop within a couple of days. Pain from the wound will gradually go away. The abscess should heal completely within two weeks.
Your healthcare provider may schedule a follow-up appointment to examine or repack your abscess. Make sure to keep all appointments. If you have any of the following symptoms, see your healthcare provider right away:
- Fever.
- Redness.
- Swelling.
- Increased pain.
You can prevent skin abscesses by keeping your skin clean and dry. Bacteria getting into minor wounds cause most skin abscesses. Other steps you can take to prevent skin abscesses include:
- Washing your hands frequently.
- Not sharing towels, razors or toothbrushes.
- Avoiding nicking your skin while shaving.
- Maintaining a healthy diet.
- Quitting smoking.
- Practicing good dental hygiene.
- Drink pure water to avoid amoebic liver abscess.
Preventing internal abscesses can be more difficult. They are typically complications of other conditions.
A very small abscess or one close to the surface of your skin may resolve by itself. You may be able to get rid of an abscess by applying a warm compress to the area. It may drain naturally, but you shouldn’t attempt to drain or burst an abscess at home. If you try to squeeze the pus out of an abscess yourself, it can easily spread the bacteria to other areas of your skin.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe an antibiotic. But treatment for an abscess may also require surgical drainage. First, your healthcare provider will apply a local anesthetic to the area around the abscess. With local anesthesia, you’ll stay awake but the area will be numb.
Your healthcare provider will make a tiny cut (incision) in the abscess. They’ll allow the abscess to drain and remove any remaining pus, dead tissue and debris. They’ll leave the abscess open to allow any remaining pus to drain. (For larger abscesses, they may pack the open abscess with gauze.) Then, they’ll apply a clean, dry bandage to the area. The incision will heal on its own. You may have a scar at the incision site. A scar can tell you your abscess is healing.
To get rid of an abscess on your gums, your dentist will perform a surgical drainage procedure. Depending on the severity of the abscess, they may have to perform a root canal or pull any affected teeth (extraction). They may prescribe antibiotics as well.
For internal abscesses, your healthcare provider may perform a needle aspiration. Depending on the location of the abscess, you’ll receive local or general anesthesia. Then, they’ll guide a needle into place using an ultrasound or CT scan. They’ll drain the abscess using the needle. They may make a small incision in your skin and insert a thin plastic tube called a drainage catheter. The catheter allows the abscess to drain into a bag. You may have to leave the bag in place for a week or more.
- Amclav 625 BD 5 days
- Cap Amclox 500 mg BD for 5 days.
- Tan Erythromycin 500 mg TDS for 5 days.
Sadyo Vamana is a type of purificatory measure mentioned in Ayurveda, which to expel the pus and morbid factors present in a dental abscess without opening it .The patient was given Sadyo Vamana (instant therapeutic emesis) to expel the accumulated pus in dental abscess without opening it.
Along with it, the respective correction of two doshas – the fiery Pitta and the water Kapha is also done by Ayurveda doctors.
https://madhuchhandacdmo.blogspot.com/2022/10/abscesses-pus.html







.jpg)


.jpeg)
Comments
Post a Comment