Jaundice In Newborns
Jaundice In Newborns
Jaundice in newborn babies is normal and is not serious most of the times.
Jaundice is very common in premature babies, affecting males more often than females. Approximately 60 percent of infants have jaundice While most children getting jaundice recover without much of a problem, some of them need serious attention. Doctors get really concern under the following circumstances.
Jaundice appearing within 24 hours after birth.
A child with jaundice who appears unusually sick , drowsy and anemic or one who develops altered behavior, or a bleeding tendency , or swelling of the body or persistent vomiting and dehydration.
Introduction
What is Jaundice ?
When your baby's skin turns yellow in color it's called Jaundice. The white of your baby's eye may also turn yellow. (Icterus positive) This is due to excess amount of bilirubin. The bilirubin comes from the breakdown of old red blood cells.This type of jaundice starts when the baby is 2-3 days old. It goes away by the time your baby is 2-3 weeks old. This happens about half of all babies and is not harmful. Jaundice progresses from head to toes; and it regresses from below upwards. Whites of the eyes may remain yellow for a longer period of up to 2 to 3 weeks.
This could happen for any of the following reasons;
All Baby's should be tested for "newborn screening disorders" - which sort of rule out majority of the causes, If the baby is active, passing yellow stools, most of the time, nothing else needs to be done. If these newborn screening tests have not been done, then the baby needs to be subjected to a few tests to ensure that he doesn't have Breast milk jaundice (BMJ,) there is no other reason for the same.
Causes
Normal Jaundice: Or Physiological Jaundice
There are several reasons for this
- The baby's liver is not yet ready to get rid of the yellow pigment called Bilirubin on its own.
- During birth, babies receive more blood from the placenta than they can handle immediately.
- Some babies can be bruised at birth- bruises produce more bilirubin.
- The gut morality in first few days sometimes is not that good. So babies take some time before they can 'excrete' bilirubin in the stools.
- Insufficient milk intake from exclusive breast feeding with poor milk supply.
Other causes
- Premature Birth
- Breast Milk Jaundice
- Rh Factor incompatibility
- Blood group incompatibility
- Induced labour
- Infection
- Metabolic condition such as low blood sugar
- Administration of drugs to the mother in pregnancy.
- Diseases.
- G 6 PD deficiency
- Cephalohematoma
- Thyroid deficiency or
- Galactosaemia - a rare inborn error of metabolism.
"Jaundice in newborn babies is normal and is not serious most of the times."
Physiological Jaundice
Most jaundiced babies have what is known as normal or physiological jaundice. The jaundice normally appears after 30 hours of birth, gradually deepens and disappears on the 10th day. This happens due to slight immaturity of baby's liver. The child gradually does not require any treatment.
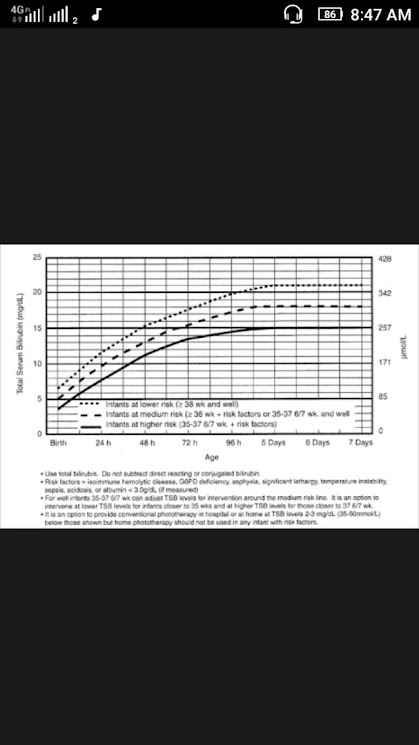
The level of jaundice is known by estimating the level of serum bilirubin (the yellow pigment produced by the breakdown of red blood cells). In physiological jaundice, the bilirubin level usually does not exceed 20 mg/dl. In Indian and other Asian children, it may reach 25 mg/dl without causing any problem to the child.
In case of high levels, your doctor may like to estimate the level of hemoglobin and may again test for bilirubin. Arise of 0.5 mg/dl of bilirubin are more per hour or a falling hemoglobin level may need some intervention. Children who are born normally without any problem are usually quite safe, but those who are born prematurely or had lack of oxygen, low blood sugar or accumulation of acids in the body (acidosis) needs extra care.
Some jaundiced babies are sleepy and may not suckle too well are too often.
- Physiological Jaundice appears on the second day of the birth, reaches peak on the 4th or 5th day and disappears by 8 to 10 days.
- The best management of physiological jaundice is exposing the baby to sunlight for about 10 to 20 minutes. IF necessary photo therapy can be given.
- While exposing the baby to sunlight, baby's eyes and perineal area should be covered.
Physiological Jaundice is fairly common, mild and usually harmless. Within the uterus the baby has an abundance of red blood cells. Once the baby is born and breathing, an excessive amount of red blood cells is not needed, so they break down until the level of cells is appropriate for the baby. A by-product of the breakdown of bilirubin, which deposits in the skin and is evident as yellow coloring.
It is more common in induced labour, as it causes strong contractions, which can cause just before birth, an abnormally large amount of blood to be shunted to the baby. Extra blood means extra red blood cells, which predisposes the baby to jaundice.
Management
Frequent suckling is the best way to reduce the incidence of jaundice and to treat it as well. Bilirubin is present in large amounts in the meconium- the baby's first stool. If the meconium is not cleared , the bilirubin gets absorbed into the baby's system. Colostrum (the first breast milk) helps to clear meconium and thus assists in the prevention of jaundice. If your baby gets enough breast milk , it helps to clear early jaundice. Giving glucose water, plain water or other supplements does not help. Such drinks interfere with breast feeding and an increase the jaundice.
The best way you can help your baby with jaundice is by breastfeeding him frequently, whenever he is hungry (demand feeding) during the day and night . If he is unusually sleepy , try to stimulate him every 2 hours. If he does nor oblige, report to your doctor who may ask you to express your milk and give it to the baby with a small glass or bondla (Paladai) every 3 hours.
Late Onset Jaundice in a Newborn Baby
Sometimes, jaundice starts at the end of the first week of life in an otherwise healthy baby and may last up to 3 to 10 weeks of age. Often, this prolonged jaundice is not serious and is due to the presence of a harmless substance in the mother's milk. That is why it is also sometimes labelled 'breast milk jaundice' It tends to reoccur in the next child. The jaundice is harmless and clears without any treatment.The baby continues to suckle well and gains weight normally.. If the jaundice is very severe, especially if the baby looks unwell, your doctor may consider the possibility of the child having some other conditions.
Treatment
The doctor may temporarily stop the breast feeding to confirm the diagnosis of late onset jaundice.. This would bring down the levels quickly, but do not agree to this suggestion too readily. In such a situation you have a following options:
- Express your milk, boil it and give it to your baby by a bondla. Heating breast milk reduces the level of bilirubin.
- Stop breastfeeding temporarily for 12 to 48 hours and give breast milk from another HIV -negative mother or from a "breast milk bank." Keep expressing your milk and discard it.
- Alternate artificial milk feeding and breast feeding for 24 to 48 hours.
- Continue breastfeeding normally and give photo therapy.(light therapy).
- Replace breastfeeding by artificial milk feeding for 12 to 48 hours while observing the reduction of bilirubin and the level of jaundice.
Very high level of bilirubin can cause damage to the brain of a new born baby. But no such damage has ever been reported due to late onset of jaundice .
It is important to realize that even if a baby needs treatment (usually light therapy) for jaundice, you must continue to breastfeed your baby normally.
Feeding colostrum to the baby helps the baby to pass its first stool, which contains lot of bilirubin, which, if not quickly excreted, can be reabsorbed into the baby's blood stream. This is how colostrum may help prevent physiological jaundice. Hence colostrum should be fed to the baby. The hospital might give a jaundiced baby plenty of water to flush out its system. If this is the case , you should express colostrum or milk after or between feeds with your hands, since the baby whose thirst a slaked with water will reduce sucking. Your expression will stimulate and keep up your milk supply.
Physiological jaundice normally appears after 30 hours. Peak level of bilirubin reached on the forth or fifth day and eyes return to the normal color by the seventh day. In physiological jaundice the bilirubin level normally does not exceed 10 mg/ ml.
Premature Birth
Babies born prematurely may have underdeveloped organs and have even more difficulty removing bilirubin from their bodies than full term babies, resulting in jaundice
Breast Milk Jaundice
Breastfed newborns can develop jaundice from certain chemicals in breast milk, which can prevent the liver from excreting bilirubin effectively. This condition is harmless and resolves on its own over 3-12 weeks
It is normal for breast feeding babies to have jaundice. It usually occurs at 10-21 days of age and can last for 2-3 months. As long as the baby is gaining weight, passing lots of clear yellow urine and yellow or green stools, and having bowel movements, there is no need to be worried. It is not harmful, therefore do not stop breast feeding. BMJ is a sort of diagnosis of exclusion.
This is rare kind of jaundice that develops about one week after birth and could continue for two months. Although jaundice can become as deep as 20 mg bilirubin / 100 ml of serum. It does bot harm the baby's brain, but it occurs after the first week of life, when the blood brain barrier is reasonably well developed. You can continue breast feeding.
However if your baby's bilirubin rises too high, your pediatrician may request you to interrupt breastfeeding for a while, say six to twelve hours. If at the end of this time the bilirubin level has fallen for more than say 2 mg per 100 ml of serum, breast feeding can be resumed.. Usually the bilirubin level rises slightly before falling slowly and steadily. If the level rises during the break or breaks, the jaundice is not being caused by the breast milk, and other causes need to be investigated. Generally jaundice is no cause to stop breastfeeding. Some people wrongly believe that breast milk jaundice means that breast feeding should be completely stop. This is not so. The condition resolves spontaneously in time, with no ill effects on the baby from breast milk.
Induced labour
It is more common in induced labour, as it causes strong contractions, which can cause just before birth, an abnormally large amount of blood to be shunted to the baby. Extra blood means extra red blood cells, which predisposes the baby to jaundice.
Jaundice Due To Blood Group Incompatibility
Rh incompatibility and A.B.O incompatibility between the mother and the foetus can result in jaundice in the newborn baby.
Your doctor will get your blood tested during pregnancy to find out if you are Rh negative. If so, your baby will be observed closely for appearance of jaundice and for the rate of rise of bilirubin and his level of hemoglobin. Your doctor may also give you a special injection within 24 to 72 hours after delivery to prevent any trouble to your next baby.
A.B.O incompatibility is a relatively milder disease. The common combination is an O group mother and A or B group fetus.
Mismatched Blood Type
This is a rare cause of jaundice in newborns. But if the baby has a different blood type than its mother, the antibodies in her body will start to attack the baby’s red blood cells
Rh or A.B.O problems; Jaundice can happen in if the baby and mother have different types of blood group types. There are two different types of blood group incompatibility that can cause Jaundice. When the mother's blood group is 'o' Positive and the baby's group is A, B,or AB positive; when the mother's blood type is negative and the baby's blood type is positive, jaundice can occur in baby.
Therefore every baby's blood group,should be checked routinely, so that one is sure if the case arises. This type of Jaundice most often starts from the first day of the baby's life.
That is jaundice that occurs in the first 24 hours. It is more severe and serious and is called haemolytic jaundice. It may be the result of blood group incompatibility between the mother and the baby and needs urgent treatment to prevent brain damage in the child. The baby needs to be treated in the hospital. It may require complete exchange transfusion of blood, after which breastfeeding can continue normally.
R.H Incompatibility
It is quite safe to feed your baby even if your blood group is rhesus-negative. and your baby is rhesus-positive. Rhesus antibodies are present in breast milk if they are present in the mother's blood, but they get inactivated by digestion in the baby's gut; therefore you can safely feed the baby. It is also quite safe to breast feed after having an injection of Anti D Immunoglobulin.
Other causes of Jaundice in new born
Any Jaundice that persists for over two weeks may need detailed investigations. If the child has white stools, it may be due to the flow of bile being obstructed. Such a child needs the urgent attention of a pediatric surgeon.
Jaundice in older children
Causes
The two common causes of jaundice in older children are infections or drug affecting the liver. Certain drugs given for tuberculosis and epilepsy can cause jaundice. The common infections causing jaundice are hepatitis and malaria. In malaria, the child with jaundice may have very low hemoglobin. He is often very anemic and may need hospitalization and blood transfusion.
Cephalohematoma
If doctors use tools during delivery, it can break the blood vessels under the scalp. If the blood builds up under the skin, there may be an increase in bilirubin and increase the risk of jaundice. Cephalohematoma occurs in 1 to 2 percent of all live births
Cephalhaematoma is a localized swelling of the head in a new born baby- which may appear soon after birth or in the first 3-4 days of life. This is due to collection of blood between your baby's skull bones and a tough thin tissue called the periostium, which surrounds the bone (almost like a shrink wrap). Cephalhematoma most commonly occurs over the parietal bone. It can happen during normal deliveries or more commonly following instrumental deliveries like forceps and vacuum. Some times you may see after a caesarean section, as some doctors use a vacuum to get the baby's head out since a baby's head tends to be very slippery. This is a temporary swelling, it usually last for 3-4 weeks and generally disappear with time. If they are huge then they may cause increased chances of higher jaundice or sometimes, rarely, can get calcified, leading to a bump, which becomes less obvious as the baby grows, since 90 % of the head growth happens in the first two years of life.
Diagnosis
When diagnosing jaundice, the doctor will ask about the patient’s symptoms and health history before performing other exams .
Blood Test
- Complete blood count (CBC) – measures the components of the blood, including platelet levels, white blood cells and red blood cells
- Bilirubin blood test – measures bilirubin levels . When your baby looks jaundiced, a blood test is done to check the level of bilirubin and to help find the cause.
- Behold The Bili - Ruler : A novel low cost devise for screening neo-natal jaundice.
Symptoms of Jaundice
- Infant with jaundice will have difficulty in feeding.
- Irritability
- Inability to gain weight
The main sign of jaundice is yellowing of the skin and eyes. Some symptoms differ between short-term and more severe cases or between adults and infants. In addition to yellowed skin and eyes, some common symptoms include
Kernicterus
This condition develops in newborns when severe jaundice goes untreated and bilirubin spreads to the brain
Extent of Jaundice
If the condition is mild, it may resolve itself. Infant cases can be more severe.Treatment usually aims to alleviate the cause of the condition rather than just the symptoms by
- Feeding infants more often to produce more waste and flush bilirubin
- Pumping, rather than breastfeeding, breast milk
- Photo-therapy
- Blood tests
- Exchange Blood transfusion
- Removing any obstructions
Supplements for Jaundice
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
Vitamin B 2 is used to treat neonatal jaundice. Riboflavin is a light-sensitive vitamin used in phototherapy
Vitamin B12
Yellowing of the skin is often caused by Vitamin B12 deficiency. Increasing Vitamin B 12 intake could be the simplest solution to reduce the appearance of jaundice
Vitamin D
Low Vitamin D levels has been linked to the progression of certain liver diseases and, as a result, jaundice. Keeping stable levels of Vitamin D can help control the symptoms of liver problems including yellowish-skin
Breastfeeding
Feed your baby often, this can help lower the bilirubin. If you are breastfeeding, feed your baby every 1 1/2 to 2 1/2 hours during the day.To increase the milk flow, massage your breast towards your nipple,as the baby sucks.
Formula Feed
If you are bottle feeding, feed your baby every 2 to 3 hours during the day. If your baby sleeps more than 4 hours at night, wake the baby up for feeding. Babies with Jaundice are often very sleepy. try to keep your baby awake for feedings by stroking his chin, lifting the arms up and down or changing the diaper and washing his face.
Exposure to sunlight
Lots of parents ask about exposure to sunlight. Photo-therapy was discovered a dew decades ago in Scandinavian countries where babies in winter had more Jaundice than babies in summer, hence sunlight is the answer, but sunlight can have harmful rays too. Therefore place your baby near a bright,sunny window if possible during early morning hours only, but ensure that your baby does,'t get sunburn on hot days and doesn't get cold on cold or rainy days.
If your baby is otherwise well your pediatrician will agree to your taking the baby home and giving it exposure to sunlight. You can place the baby naked next to the window but make sure he /she does not get too hot or too cold. You can blind fold the baby if the sunlight is too strong, so that it does not affect baby's eyesight. You may have to take your baby back to hospital for blood test.
Photo Therapy (Light Therapy)
Light therapy (photo therapy) is based on the principle that exposure of the skin to blue or florescent tube light, or day light converts bilirubin in a manner that it can be eliminated more easily from the body.
The baby is put under the light without clothes, with his eyes covered to prevent damage. The light is kept approximately 45 cms above the infant.Avoid undue separation from your baby, you can request the nursing staff to bring the photo-therapy unit next to your bed.
Some babies may get loose motions while under the lights. This is normal. Others become a little irritable to begin with. Some may develop the so - called 'dehydration fever' due to loss of water from the body. You may be tempted to give water to the baby for this reason. This should be avoided. Frequent breastfeeding will provide the required amount of fluids in most cases.
One way to reduce the level of jaundice is to expose the baby's skin to light, a process called phototherapy. We have specialized lights called "biliblankets & LED lights'- which help in treating jaundiced babies and with these new technologies - the spread at which bilirubin comes to normal levels is much faster; also the baby stays with his mother rather than being separated as in most hospitals.
The lights change the bilirubin, so that the kidneys can get rid of it rather than the liver, which can be under developed with newborn babies. The babies eyes are covered to protect them from the bright light. Your baby may have skin rashes or loose greenish bowel movements. This is temporary and should stop when the photo-therapy is discontinued. Photo-therapy is safe but is used only when needed. Your baby's pediatrician will look at the baby's blood test results and decide how long he needs to be under photo-therapy.
Babies with moderately raised bilirubin are often treated by being placed uncovered in a cot sixteen inches beneath a day light fluorescent tube with their eyes covered. This is called photo therapy. There is no harm if you take baby from under the light every two hours to feed, and may be more often if he/she demands it. Remove the eye cover when you feed
While your baby is off breast milk, keep your milk supply by going by expression or pumping more frequently than your baby would have fed, and discard your milk until your milk can again be fed.
Vitamin D drops 1 ml per day.
Exchange Transfusion
An exchange transfusion is undertaken mostly in Rh incompatibility if the hemoglobin estimation of the cord blood of the baby is low or his cord bilirubin is high, or if the bilirubin levels after birth cross the safe levels.
It may also have to be undertaken in certain other situations like a premature baby whose bilirubin levels rise rather rapidly or babies with jaundice who also have added problems like infection, low blood sugar etc.
https://madhuchhandacdmo.blogspot.com/2020/12/jaundice-in-newborns.html














Comments
Post a Comment